How and Where to Buy the Best Lab-Grown Diamonds

Interested in purchasing a lab-grown diamond? You’re not alone – more people than ever are choosing lab-grown diamonds over natural diamonds. And it’s no wonder why – lab-grown diamonds offer the same beauty as natural diamonds, but for a fraction of the cost. In fact, lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds and will test as a real diamond. This guide will teach you where and how to find the best lab-grown diamonds.
Choosing the Right Lab Diamond
The best way to get a high-quality yet affordable lab-grown diamond is to learn about the 4 Cs. It’s also extremely important to research your potential diamond’s certifying agency to make sure that it is reliable. Let’s start by going over the 4 Cs.
The 4 Cs
The 4 Cs are an industry-wide method of measuring the beauty and value of a diamond. The 4 Cs are Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat. By understanding the 4 Cs, you’ll be able to choose the best, most beautiful diamond for your budget.
Cut
Cut is often considered the most important of the 4 Cs. An expertly cut diamond will be full of sparkle and brilliance; a poorly cut diamond will look dull and won’t reflect much light. Diamonds can receive one of the following cut grades: Ideal, Very Good, Good, and Poor.
Ideal Cut

Ideal-cut diamonds are engineered for maximum light return and have excellent polish and symmetry. This cut grade is only achievable for round-cut diamonds; fancy shapes (any shape that is not round) cannot receive an Ideal cut grade. Since this is the highest-quality cut grade, it will also be the most expensive.
Very Good Cut

Diamonds with a Very Good cut will provide ample sparkle. These diamonds have great polish and symmetry.
Good Cut

These diamonds have a good amount of sparkle and adequate polish and symmetry.
Poor Cut

Diamonds with a poor cut won't have much sparkle, and can even face up smaller. Ritani does not offer diamonds with a poor cut.
Choose the best cut grade for your diamond – for a round cut, choose an Ideal cut, and for a fancy shape, choose a Very Good cut. You should also make sure your diamond has Excellent polish and Excellent symmetry for maximum beauty and scintillation.
Color
A diamond’s color grade measures how little color it reflects. Some diamonds naturally have a faint or noticeable yellow hue. Diamonds are graded on a scale of D to Z – D being completely colorless, Z having noticeable yellow or brown color. Most shoppers seek diamonds that appear colorless.
At Ritani, we recommend near-colorless diamonds, which will face up as white but will still help you save hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
Colorless Diamonds (D, E, F)
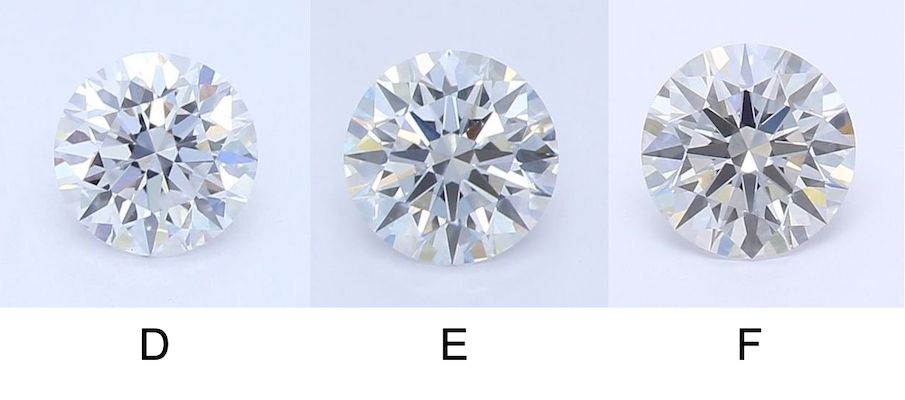
Colorless diamonds (D, E, and F) are completely white. They are very rare, and thus the most expensive. Colorless diamonds pair best with silver-colored metals like platinum and white gold.
Near-Colorless Diamonds (G, H, I, J)
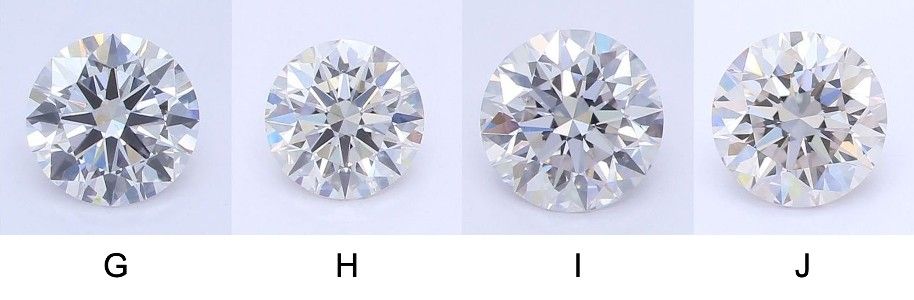
Near-colorless diamonds pair well with any metal, including rose and yellow gold. These diamonds will face up as white, but are far less expensive than colorless diamonds, making them a wise purchase.
Noticeable Color (K, L)

These warmer-toned diamonds have a faint-yellow hue and pair best with rose or yellow gold. Even though the diamond color scale goes from D to Z, Ritani does not carry diamonds below L.
Clarity
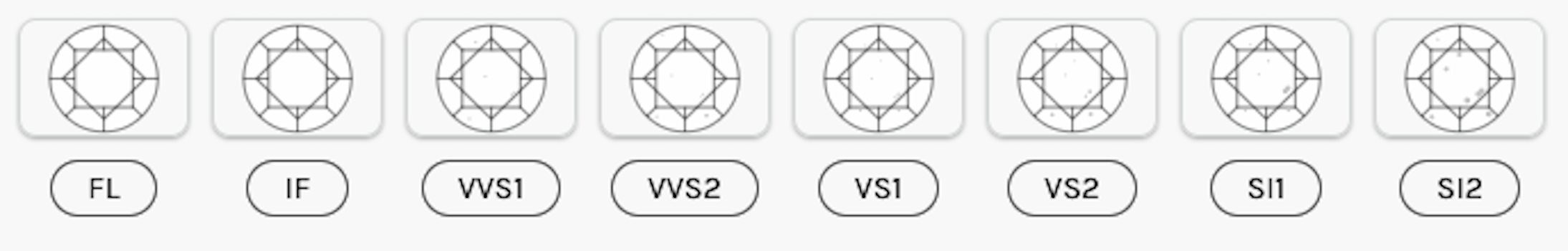
Clarity refers to how many (or how few) inclusions a diamond has. Inclusions are tiny imperfections on the inside of the diamond. Too many inclusions can detract from the beauty of a diamond.
Flawless (FL)

Flawless diamonds have zero inclusions or blemishes. Not only are Flawless lab-grown diamonds very rare as they are difficult to create in a laboratory setting, but they would be quite expensive if you could find one.
Internally Flawless (IF)

Internally Flawless diamonds have no visible inclusions but may have blemishes. Blemishes are external flaws that can occur from cutting or setting the stone. Internally Flawless diamonds are also rare, making them more expensive to purchase.
Very Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2)

VVS diamonds have very few inclusions visible under 10x magnification. They will be eye clean.
Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2)
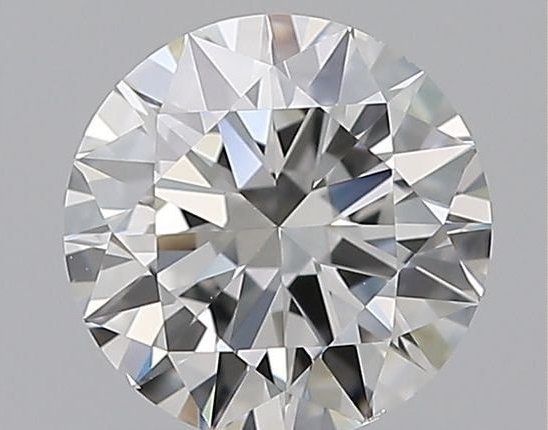

VS1 and VS2 diamonds have a few more inclusions than VVS diamonds, but will still be eye clean.
Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2)
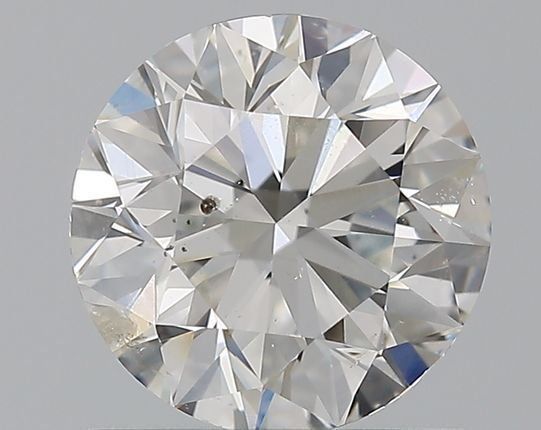

SI1 and SI2 diamonds have small imperfections that may be visible to the naked eye. Slightly Included diamonds are sometimes eye clean, but are not always, so pay attention to where and how large the stone's inclusions are. Pass on diamonds with inclusions at the center of the stone's table.
To make sure your diamond is eye clean (eye clean diamonds do not have inclusions visible to the naked eye) choose a minimum clarity grade of VS2. It’s also essential that you view HD images and videos of your diamond before purchasing it.
Carat

Carat is the measure of how much a diamond weighs. One carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams, or 200 milligrams. Carat is also related to how large the diamond will look, but it’s not a 100% reliable indicator since many factors can affect how large a diamond looks. Carat has a huge influence on the price of a diamond as larger diamonds are rarer. Here are some of the most common carat weights purchased:
1 Carat Diamonds
A 1-carat round-cut diamond will measure approximately 6.5 mm in diameter, but this can vary depending on how well the diamond was cut. 1-carat is the nationwide average for diamond engagement rings, but the size you choose for your ring really depends on your personal preferences as well as your budget. Luckily, since lab-created diamonds are far more affordable than natural diamonds, you can choose a larger diamond for your budget if that is what you desire.
Discover 1 Carat Lab-Grown Diamonds
1.5 Carat Diamonds
Slightly larger than a 1-carat diamond, a 1.5-carat round-cut diamond will measure about 7.4 mm in diameter depending on how well the diamond was cut.
Discover 1.5 Carat Lab-Grown Diamonds
2 Carat Diamonds
A 2-carat round-cut diamond will measure about 8.1 mm in diameter, again, depending on the diamond's cut quality.
Discover 2 Carat Lab-Grown Diamonds
3 Carat Diamonds
A 3-carat diamond is a standout choice. A 3-carat round-cut diamond will measure approximately 9.3 mm in diameter. Diamonds of this size will have easier-to-detect inclusions, so pay extra attention to the clarity grade and location of inclusions in your diamond.
Shop 3 Carat Lab Grown Diamonds
4 Carat Diamonds
This luxurious diamond size is now more attainable thanks to the reduced costs of lab-grown diamonds. A 4-carat diamond will measure about 10.4 mm in diameter.
Shop 4 Carat Lab Grown Diamonds
Pro Tip
Since carat has a large influence on the price of a diamond, we recommend "buying shy". This means that if you are interested in purchasing a 1-carat diamond, go for a diamond in the 0.9 carat range instead. These diamonds will appear to be the same size as a 1-carat diamond, but are more affordable.
Diamond Shapes
Sometimes, a diamond's shape is also referred to as its cut. For example, "pear-shaped lab-grown diamond" and "pear-cut lab-grown diamond" are used interchangeably. Diamond shapes are not part of the 4 Cs, but can still have an impact on the price of your diamond. The shape of your diamond will have a huge impact on the vibe and personality of your jewelry piece. At Ritani, we offer 10 different lab-grown diamond shapes, but these are the most popular:
Round-Cut Diamonds
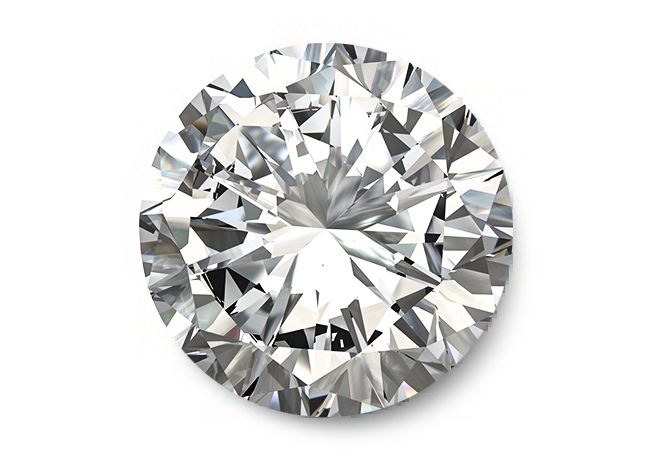

This is the #1 most popular shape of all time for engagement rings, pendants, earrings, bracelets, and any other jewelry piece you can think of thanks to its versatility and timelessness. This shape also holds the title of being the most sparkly. Round-cut diamonds are the most expensive shape due to their popularity and amount of diamond waste produced while they are being cut. If you are on a budget, or maybe just want something more unique, you may want to look into fancy-shaped diamonds instead.
SHOP ROUND-CUT LAB GROWN DIAMONDS
Cushion-Cut Diamonds

This timeless shape is similar to the round-cut, but with a slightly more square silhouette. Cushion-cut diamonds can vary in appearance; choose a cushion-cut diamond with a length-to-width ratio of 1.00 for a more square-shaped cushion-cut, or if you prefer the look of an elongated cushion-cut, choose a diamond with a length-to-width ratio of at least 1.1.
SHOP CUSHION-CUT LAB-GROWN DIAMONDS
Princess-Cut Diamonds
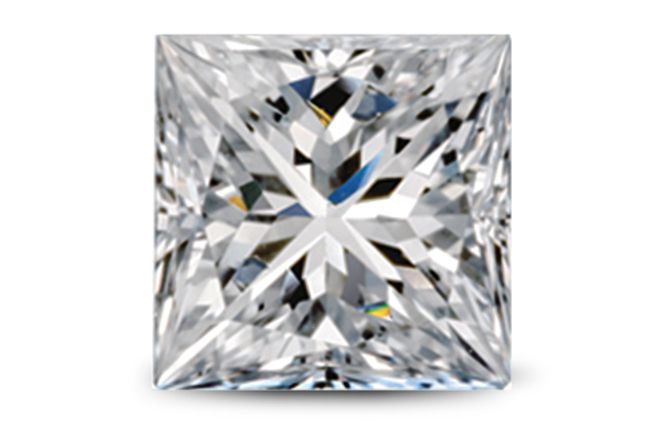

This modern, square diamond shape offers lots of brilliance. Note that due to their sharp edges, princess-cut diamonds are prone to chipping, so they are not the best choice in rings for those with active lifestyles.
SHOP PRINCESS-CUT LAB-GROWN DIAMONDS
Oval-Cut Diamonds

This elongated diamond shape has a large surface area, making it appear bigger than other shapes like the round-cut or cushion-cut. When set in an engagement ring, it produces a flattering effect on the hand, making fingers appear longer and slenderer.
SHOP OVAL-CUT LAB-GROWN DIAMONDS
Diamond Anatomy
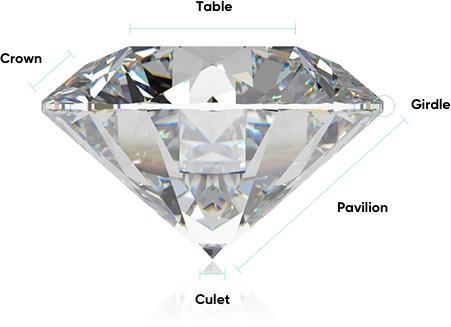
Diamond anatomy is important to understand because it can affect the quality and beauty of your lab diamond. Details regarding your diamond's anatomy can be found in its grading report.
Table
The table is the diamond's largest facet which gathers and reflects much of the light that enters the stone. A diamond's table size is typically reported as a percentage. A proper table can make your diamond appear larger, however, you don't want a table that is too large or too small. This will affect the diamond's sparkle as well as its cut grade. The ideal table percentage will vary depending on diamond shape. Below is the ideal table percentage for each shape:
| Diamond Shape | Ideal Table % |
| Round | 54-57% |
| Cushion | 61-68% |
| Princess | 69-75% |
| Oval | 53-63% |
| Emerald | 60-68% |
| Radiant | 61-69% |
| Pear | 53-65% |
| Marquise | 53-63% |
| Heart | 54-66% |
| Asscher | 53-63% |
Crown
The crown angles downwards and connects the table and girdle. The crown can affect your diamond's visual size. Look for diamonds with a crown angle of 32 to 36 degrees.
Girdle
The size of the diamond's girdle will impact its durability; if the girdle is too thin, the diamond may be more prone to chipping. However, you also don't want a girdle that is too thick because it can affect the stone's light performance and make the diamond look smaller. Look for diamonds with a girdle in the Thin to Slightly Thick range.
Pavilion
The pavilion is the angled bottom half of the diamond. This part of the diamond will affect the stone's brilliance and fire. The best pavilion depth percentage is between 41-48%. Anything shallower can affect the stone's light return. Pavilion angle is also important; look for diamonds with angles between 37 and 44 degrees.
Culet
The culet (pronounced cue-let) is the bottom part of the diamond. Not all diamonds have a culet. Look for diamonds with the following culets: None, Small, or Very Small.
CVD vs HPHT Diamonds
There are two processes in which lab-grown diamonds are made: the CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) process and the HPHT (High-Pressure High Temperature) process. Both processes will yield a beautiful diamond. Most diamond grading reports will specify the process in which your diamond was formed.
However, it’s important to note that some HPHT diamonds will have what is called a blue nuance. This blue nuance is a faint blue tint in the diamond that is caused by excess boron. This doesn’t mean you have to avoid HPHT diamonds – some think this effect is unique and interesting. It just means that it’s very important to view imagery and/or videos of your diamond before purchasing it. When in doubt, contact our diamond concierge team and we can help you identify the blue nuance in HPHT lab diamonds.
LEARN MORE ABOUT CVD VS HPHT DIAMONDS
Diamond Certification Labs
Gemological laboratories will grade diamonds for their quality. They will grade a diamond’s cut, color, clarity, and cut, as well as many other factors, such as the diamond’s fluorescence levels, proportions, and more. Laboratories can also determine the origin of a diamond (lab-grown or earth-grown) as well as the method in which the lab diamond was made.
Choosing a diamond that was graded by a reputable agency will help you get a truly high-quality lab diamond. Here are some of the best laboratories to choose from that grade lab-grown diamonds.
GIA Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) is considered one of the top diamond certifying agencies. This is because it is reliable and consistent; it is the toughest when it comes to grading cut, color, and clarity. You can trust that their assessment of your diamond is accurate. However, GIA-certified lab-grown diamonds are a little harder to find.
Shop GIA Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
GCAL Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
GCAL (Gem Certification and Assurance Lab) is a reputable, reliable lab that is generally consistent with the GIA. GCAL reports also include a light performance profile, which analyzes the diamond’s optical brilliance and optical symmetry. This analysis will help you understand how much your diamond will sparkle.
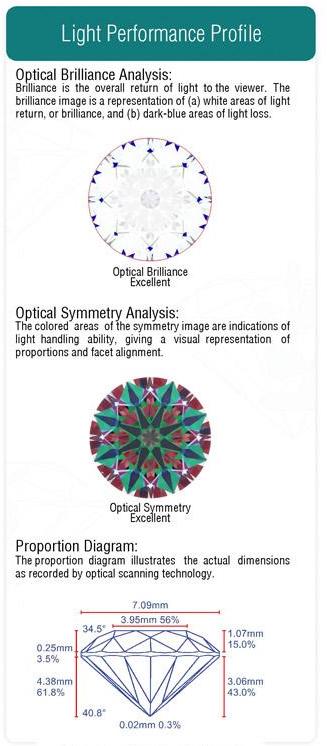
GCAL also includes Gemprint in its reports, which is essentially your diamond’s unique “fingerprint.”

Gemprint can help you identify and recover your diamond if it is ever stolen. Many insurance companies offer a discount for diamonds with Gemprint.
We recommend viewing HD imagery and/or videos of your GCAL certified diamond before purchasing it to ensure its color and clarity grades are consistent with its report.
Shop GCAL Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
IGI Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
The IGI (International Gemological Institute) grades many of the lab-grown diamonds on the market. While the IGI is generally good, it’s not as strict as the GIA. For example, an IGI-graded diamond may receive a G color grade, when in reality it is an H-color diamond. Because of these slight inconsistencies, it’s essential to view HD imagery and/or videos of your IGI-certified lab diamond before purchasing it to make sure it isn’t too yellow or too included for your tastes.
Shop IGI Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
Research Your Jeweler
No matter where you are purchasing your lab-grown diamond from, whether it is from a brick-and-mortar jeweler or an online jeweler, it’s important to do research on them first. Check out reviews to learn about other customers’ experiences and research their return and exchange policy. You should also check to see if the jeweler offers a lifetime warranty on their products.
At Ritani, we are proud to share that we have 4.5-star reviews on Trustpilot and Google. We also offer Free In-Store Preview, which allows you to preview your loose lab-grown diamond or lab diamond engagement ring at a jeweler or WeWork near you. This service is completely free – if you’re not impressed with the diamond or ring, there is no obligation to purchase it.
Final Thoughts
Since lab-grown diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds, shopping for a lab-grown diamond isn’t too different, so don’t sweat it. At Ritani, we have a vast collection of almost 50,000 lab-grown diamonds that you’ll love in all shapes and sizes. Our non-commissioned virtual gemologists are always ready to give advice and help you find the best lab-grown diamond.
Discover the Best Lab-Grown Diamonds Today


